从《系统之美》到经典控制论
当我们谈论复杂系统时,德内拉·梅多斯的《系统之美》提供了一套理解动态问题的语法,而经典控制论则赋予我们分析和设计系统的数学语言。这两者结合,形成了一条从理解到驾驭动态系统的完整路径。
当我们谈论复杂系统时,德内拉·梅多斯的《系统之美》提供了一套理解动态问题的语法,而经典控制论则赋予我们分析和设计系统的数学语言。这两者结合,形成了一条从理解到驾驭动态系统的完整路径。
- C. Forster, L. Carlone, F. Dellaert, and D. Scaramuzza, “On-Manifold Preintegration for Real-Time Visual--Inertial Odometry,” IEEE Trans. Robot., vol. 33, no. 1, pp. 1–21, Feb. 2017, doi: 10.1109/TRO.2016.2597321.
- Z. Yang and S. Shen, “Monocular Visual–Inertial State Estimation With Online Initialization and Camera–IMU Extrinsic Calibration,” IEEE Trans. Automat. Sci. Eng., vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 39–51, Jan. 2017, doi: 10.1109/TASE.2016.2550621.
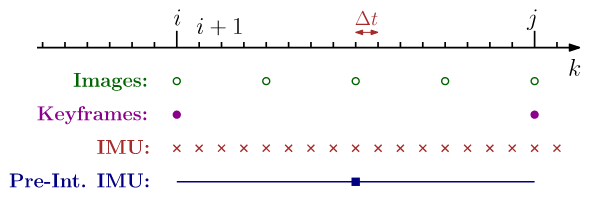
IMU preintegration is a technique in visual-inertial odometry that efficiently fuses high-frequency IMU data between keyframes. Using Lie group theory on \(SE(3)\), it handles nonlinear 3D rotations and precomputes motion constraints for optimization. This method accounts for sensor biases, noise, and is essential for real-time state estimation.
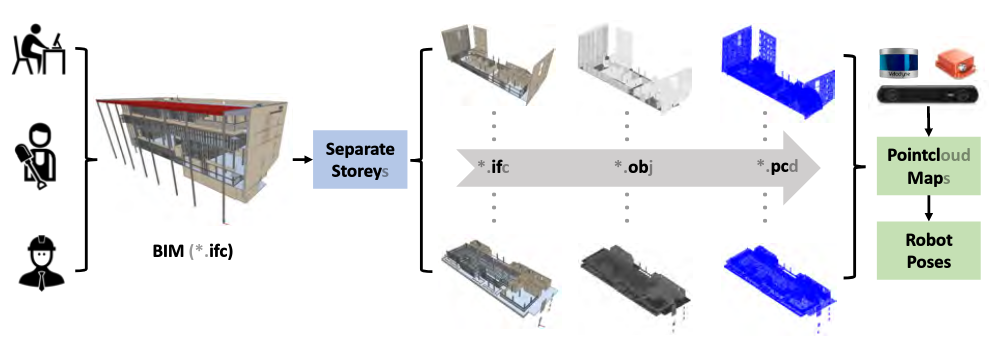
- H. Yin, J. M. Liew, W. L. Lee, M. H. Ang, Ker-Wei Yeoh, and Justin, “Towards BIM-based robot localization: a real-world case study,” presented at the 39th International Symposium on Automation and Robotics in Construction, Jul. 2022. doi: 10.22260/ISARC2022/0012.
- H. Yin, Z. Lin, and J. K. W. Yeoh, “Semantic localization on BIM-generated maps using a 3D LiDAR sensor,” Automation in Construction, vol. 146, p. 104641, Feb. 2023, doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2022.104641.
- Z. Qiao et al., “Speak the Same Language: Global LiDAR Registration on BIM Using Pose Hough Transform,” IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, pp. 1–1, 2025, doi: 10.1109/TASE.2025.3549176.
In traditional SLAM, mapping and localization occur simultaneously, with maps built incrementally. In construction, maps are created once to support long-term operations, and BIM is increasingly favored over CAD. The following studies explore BIM-based localization, semantic consistency, and geometric consistency.
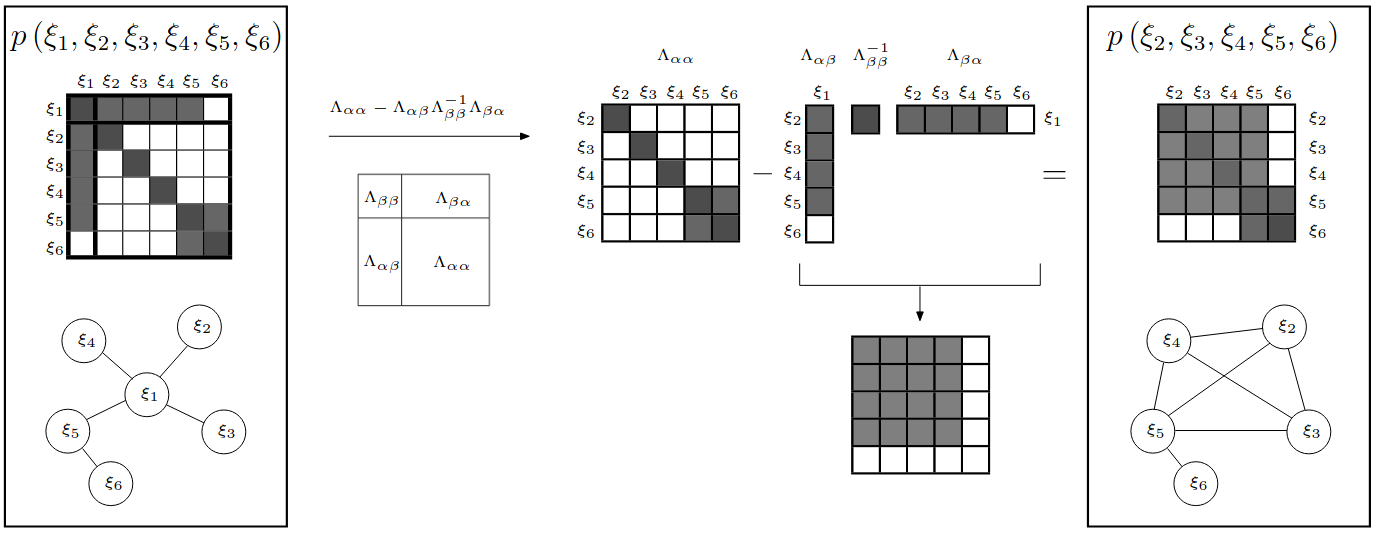
M. R. Walter, R. M. Eustice, and J. J. Leonard, “Exactly Sparse Extended Information Filters for Feature-based SLAM,” The International Journal of Robotics Research, vol. 26, no. 4, pp. 335–359, Apr. 2007, doi: 10.1177/0278364906075026.
稀疏扩展信息滤波器(SEIF)SLAM 是一种计算高效的同时定位与地图构建(SLAM)方法。通过利用信息矩阵的稀疏性,SEIF 降低了状态估计的计算复杂度,使其适用于大规模环境。
This is the lecture notes for 'ELEC 5650: Networked Sensing, Estimation and Control' in the 2024-25 Spring semester, delivered by Prof. Ling Shi at HKUST. In this session, we will cover Linear Quadratic Regulator (LQR) theory and its applications in control systems.
This is the lecture notes for "ELEC 5650: Networked Sensing, Estimation and Control" in the 2024-25 Spring semester, delivered by Prof. Ling Shi at HKUST. In this session, we will deviate Kalman Filter from three different perspectives: Geometric, Probabilistic, and Optimization approaches.
This is the lecture notes for "ELEC 5650: Networked Sensing, Estimation and Control" in the 2024-25 Spring semester, delivered by Prof. Ling Shi at HKUST. In this session, we will explore maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimation, minimum mean squared error (MMSE) estimation, maximum likelihood (ML) estimation, weighted least squares estimation, and linear minimum mean square error (LMMSE) estimation.
This is the lecture notes for "ELEC 5650: Networked Sensing, Estimation and Control" in the 2024-25 Spring semester, delivered by Prof. Ling Shi at HKUST. In this session, we will cover essential mathematical tools and concepts from linear algebra, matrix theory, and system theory that are fundamental to networked sensing, estimation, and control.